Refractive Errors
Nearsightedness (Myopia)
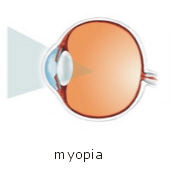
A vision condition where images of distant objects are focused in front of the retina. Therefore, near-sighted people see distant objects out of focus. People who are near-sighted can see up close more clearly than they can see objects in the distance. This kind of refractive anomaly requires a minus (negative or concave) lens for correction.
Farsightedness (Hyperopia)
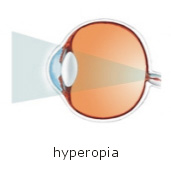
A vision condition where concentration and focusing on near objects is difficult. Images of objects are focused behind the retina causing blur vision. This kind of refractive anomaly requires a plus (positive or convex) lens for correction.
Astigmatism
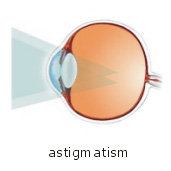
A vision condition where the vision is blurred due to the irregular shape of cornea and/or the shape of the lens. Because of this irregularity, light is not focused properly on the retina. Therefore, vision can be blurred at any distance. It can be occurred together with other vision conditions e.g. myopia or hyperopia.
Presbyopia
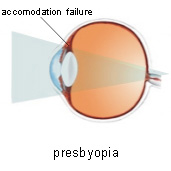
This vision condition occurs when the crystalline lens of the eye loses its flexibility and cannot focus on close objects properly. Usually the loss of flexibility takes place over years and it becomes evident in mid-40s. Presbyopia is not a disease but a natural part of the aging process of the eye.